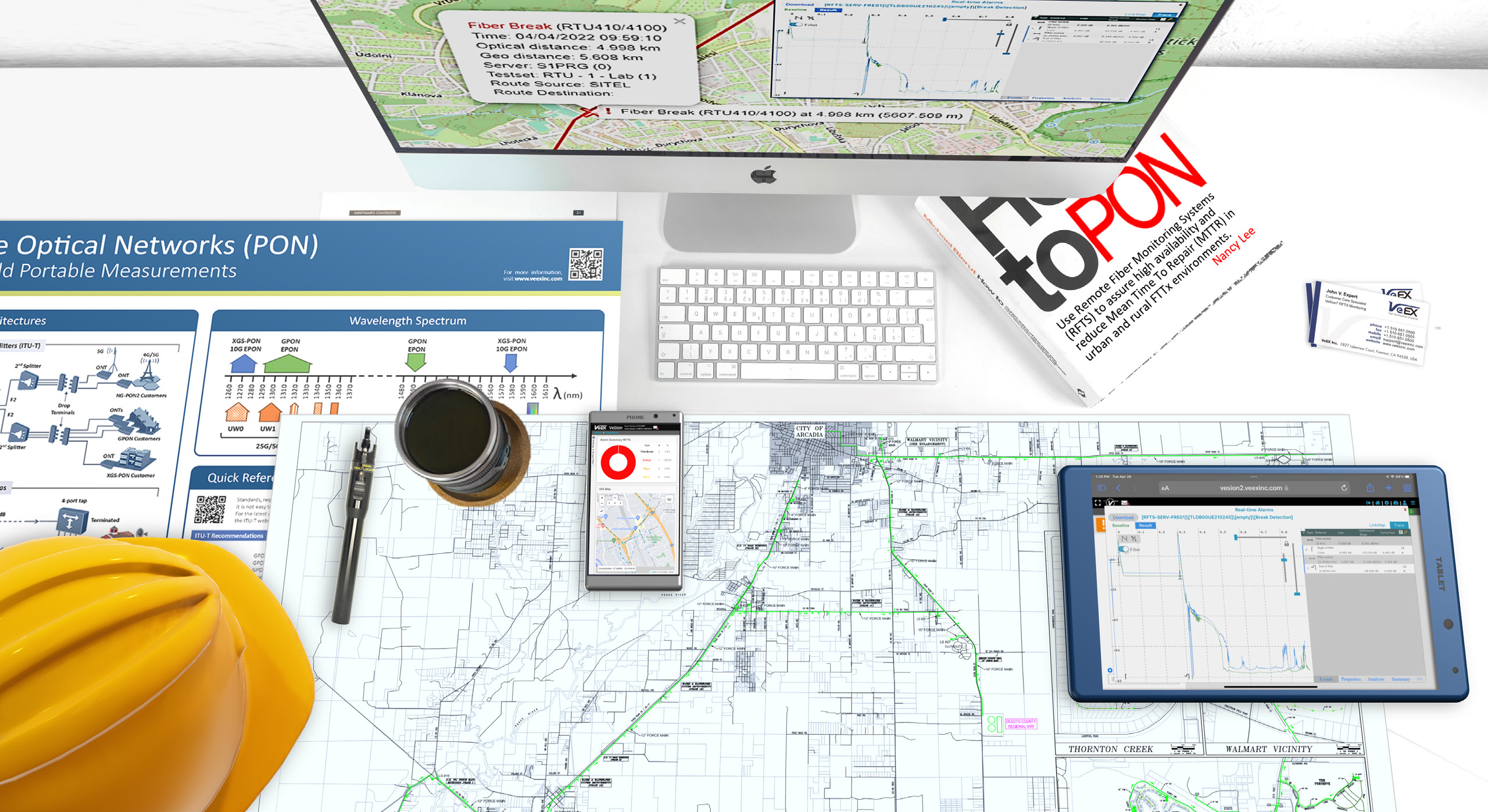
The Importance of Modern Fiber Optics Monitoring Systems
Background, Applications and Solutions (article summary)
Introduction
Fibers are a Valuable Resource
Optical fibers have revolutionized and transformed the telecommunications industry over several decades. Service Providers across the world depend on optical fiber to transmit high bandwidth data reliably over greater distances with lower loss. These key attributes make fiber the predominant and preferred choice for multiple communication applications ranging from telecom backbone infrastructure, broadband distribution, mobile X-haul, Ethernet systems, and general data networking.
Government initiatives are forcing providers to invest heavily in fiber-based networks to address the digital divide and to make working from home (WFM) both possible and efficient. Increasing the average revenue per user (ARPU) remains a key business objective but with competition increasing, network reliability is absolutely essential for customer retention.
Follow this link to download the full article (PDF)
Fiber Cuts are Costly
Service Providers constantly strive to provide fast and reliable internet service to their customers; however, a fiber break can drastically impact their ability to deliver on that promise. Fiber cuts quickly disable critical internet connections and rerouting or restoring service isn’t always fast, simple, or seamless. Service outages to fiber distribution hubs and other key data aggregation points can be very problematic as they impact a high volume of customers.
Fiber Cables are Vulnerable
What Can Damage your Cable? Private fiber networks and internet backbones are designed to be reliable, but they are not indestructible. The majority of underground and overhead cables are unguarded and unprotected exposing them to numerous threats as they traverse urban environments or travel long distances across remote/rural parts of the country. Wildlife, adverse weather conditions, sabotage, and construction work are some of the most common reasons for fiber cuts and network outages. Vehicle accidents also damage fiber infrastructure - drivers with little or no spatial awareness and people driving under the influence are usually responsible for automotive related fiber cuts.
Fiber Monitoring Solutions
Telecom service providers cannot prevent fiber cuts from occurring due to natural or human activity, but they can take steps to minimize network downtime when aerial or underground fiber cables are compromised. Reactive troubleshooting using portable field test equipment carries with it too many “risks than rewards” in today’s competitive telecom landscape - this reactive practice exposes an operator to an unpredictable amount of time to identify and pinpoint problems before fiber repairs can commence.
Fiber Monitoring is a proven, pro-active, risk-reduction and asset protection approach of pinpointing fiber degradation and breaks that threaten strategic infrastructure providing service to thousands of customers. With the ongoing deployment of high-speed Ethernet, DWDM and 5G services, it’s crucial for service providers to leverage fiber monitoring technology to protect their investment. Higher data rates and increase in channels result in more data being carried across a single fiber. Any service outage has significantly greater impact to lost revenue and reduced customer satisfaction.
Principle of Operation
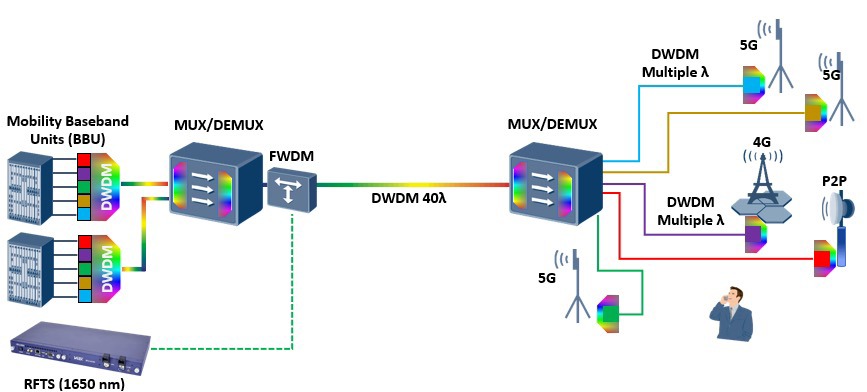
A Remote Fiber Test System (RFTS) allows service providers to monitor and troubleshoot a fiber optic network from a centralized location. An RFTS employs optical-time-domain-reflectometer (OTDR) technology to identify breaks (reactive) or other less critical event changes (proactive) on a fiber link including their precise location. Also referred to as a Remote Test Unit (RTU), this rack mount OTDR is programmed to routinely monitor fibers for anomalies or degradation that can impair optical signals, with the help of an optical switch. 
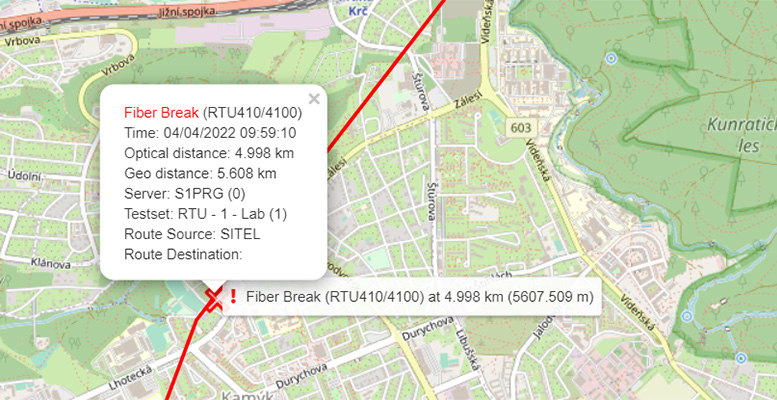
Each measured trace is compared to a reference trace of the fiber or known good baseline during normal condition – any deviation from preset thresholds is flagged as an exception and the operator is notified by text, email, and SNMP messages. The detected fault’s location is correlated on a map using a Geographical Information System (GIS) pinpointing the precise location, speeding up the dispatch and repair.
Geographic Information System (GIS)
GIS is a software platform that captures and analyzes data and displays geographically related information – it is an effective problem solving and decision-making tool used to improve the operation and maintenance of a fiber optic network. Geo-spatial data helps visualize network attributes such as cable routes, workforce, and other resources - fiber monitoring systems use this data to correlate fiber events/alarms with physical locations on a map so technicians and managers can provide more effective follow up.
VeSion® and GeoServer
VeEX offers both integrated and 3rd party GIS support options for its VeSion based fiber monitoring system. The VeSion eco-system employs a GeoServer allowing you to document your fiber route or infrastructure directly - or you can import spatial information (KML files) and other network attributes from compatible 3rd party vendor systems such as OSPInsight, IQGeo or Google Earth. GeoServer also works with freely available maps such as OpenStreetMap or any proprietary mapping data provided by the user.

The Key Components
Remote Test Unit (RTU) – comprises the OTDR hardware and software that performs the optical fiber measurement. Available in 1625nm or 1650nm filtered or 1310 or 1550nm unfiltered versions up to 45dB dynamic range.
Optical Switch – enables connection between the RTU and multiple fibers under test. Optical switches can be cascaded and/or equipped with SCA, LCA or MPO-A connectors to support very high fiber counts. Select VeEX switches offer built-in FWDM capability simplifying installation and eliminating cable routing errors, minimizing rack space requirements while also reducing optical loss.
FWDM – optical coupler combining the RTU test signal with live traffic onto the fiber to be monitored. Required for out-of-band, in-service fiber monitoring at 1625nm or 1650nm ITU-T wavelengths.
Passive Reflector – reflects the OTDR’s test wavelength only and serves as demarcation device. Used for PON construction and monitoring, to identify service handoff points of individual monitored ONT/ONUs, and/or to protect remote sensitive network equipment during live monitoring.
Servers - Depending on network complexity, service providers can choose to deploy test probes (RTUs) and optical switches at a central test location or at strategic points throughout their optical network. VeEX’s VeSion server architecture supports both centralized or de-centralized architectures and manages system information and configuration.
- VeSion Server - continuously polls RTU measurements, comparing live test data with baseline traces. Any deviations are flagged immediately, triggering powerful alarm management functions and alerts. SNMP and other protocol services support northbound communications and integration with provider’s Network Management System (NMS).
- Test Probe (RTU) Server – controls up to 75 individual fiber test probes, including measurement setup, monitoring cycles and optical switch configurations.
- Geo-Server® – supports GIS functions to pinpoint fiber cuts geographically and allows users to create and document fiber routes using spatial information (KML files). Geo-server adds value to the fiber monitoring system but is not required for the system to operate.
- R-Server® – Workflow and Asset Management system to manage teams of technicians, test equipment inventory, archive test results, create reports, streamline workforce operations, and test procedures. R-server works independent of the VeSion server architecture - although it is not required for the system to operate, it adds great value to the fiber monitoring system and repair/restoration workflow.
- Fiberizer® - embedded access within the R-server, serves as a repository for fiber test results including OTDR LinkMap and SOR files. Fiber traces can be analyzed or organized into custom collections for record keeping. Fiberizer adds value to the fiber monitoring system but is not required for the system to operate.
VeEX fiber monitoring systems are totally scalable based on customer applications and budget. Solutions can range from a single, standalone RTU that monitors a few fibers only, to a complete VeSion eco-system supporting thousands of fibers using multiple RTUs and optical switches. Ultimately the choice of monitoring system and solution depends on you, but we are at your disposal to offer expert opinion and guide you through that important decision-making process.
Follow this link to download the full article (PDF)

Related Test & Measurement Solutions
- VeEX Fiber Optics Test Solutions
- RFTS-400 - Serverless Remote Fiber Monitoring
- VeSion - Cloud-based Network Monitoring