PON Terms, Glossary & References
Common terms definitions, acronyms and references used in Passive Optical Networks documents
Table of Content
3. Standards, Specifications & Reference Documents
1. Basic Definitions
Activation: A set of distributed procedures executed by the OLT and the ONUs that allows an inactive ONU to join or resume operations on the PON. The activation process includes three phases: parameter learning, serial number acquisition, and ranging.
Bandwidth allocation: An upstream transmission opportunity granted by the OLT for the duration of the specified time interval to the specified traffic-bearing entity within an ONU.
C/M-plane: A plane of the G-PON protocol suite that handles control and management information in a G-PON system. Data on OMCI is transferred through this plane.
Dynamic Bandwidth Assignment (DBA): A process by which the optical line terminal (OLT) distributes the upstream PON capacity between the traffic-bearing entities within optical network units (ONUs), based on the dynamic indication of their activity status and their configured traffic contracts.
Embedded OAM: An operation and management channel between the OLT and the ONUs that utilize the structured overhead fields of the downstream GTC frame and upstream GTC burst, and supports the time sensitive functions, including bandwidth allocation, key synchronization, and DBA reporting.
Equalization Delay (EqD): The requisite delay assigned by the OLT to an individual ONU as a result of ranging.
G-PON Encapsulation Method (GEM): A data frame transport scheme used in G-PON systems that is connection-oriented and that supports fragmentation of the user data frames into variable-sized transmission fragments.
G-PON Transmission Convergence (GTC) layer: A protocol layer of the G-PON protocol suite that is positioned between the physical media dependent (PMD) layer and the G-PON clients. The GTC layer is composed of GTC framing sublayer and GTC adaptation sublayer.
GEM port: An abstraction on the GTC adaptation sublayer representing a logical connection associated with a specific client packet flow.
Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (G-PON): A variant of the passive optical network (PON) access technology supporting transmission rates in excess of 1 Gbit/s and based on the G.984-series of ITU-T Recommendations.
GTC adaptation sublayer: A sublayer of the G-PON transmission convergence layer that supports the functions of user data fragmentation and de-fragmentation, GEM encapsulation, GEM frame delineation and GEM Port-ID filtering.
GTC framing sublayer: A sublayer of the G-PON transmission convergence layer that supports the functions of GTC frame/burst encapsulation and delineation, embedded OAM processing and Alloc- ID filtering.
Optical Access Network (OAN): A set of access links sharing the same network-side interfaces and supported by optical access transmission systems. The OAN may include a number of ODNs connected to the same OLT.
Optical Distribution Network (ODN): In the PON context, a tree of optical fibers in the access network, supplemented with power or wavelength splitters, filters or other passive optical devices.
Optical Line Termination (OLT): A device that terminates the common (root) endpoint of an ODN, implements a PON protocol, such as that defined by [ITU-T G.984.1] and adapts PON PDUs for uplink communications over the provider service interface. The OLT provides management and maintenance functions for the subtended ODN and ONUs.
Optical Network Termination (ONT): A single-subscriber device that terminates any one of the distributed (leaf) endpoints of an ODN, implements a PON protocol and adapts PON PDUs to subscriber service interfaces. An ONT is a special case of an ONU.
Optical Network Unit (ONU): A generic term denoting a device that terminates any one of the distributed (leaf) endpoints of an ODN, implements a PON protocol and adapts PON PDUs to subscriber service interfaces. In some contexts, an ONU implies a multiple subscriber device.
Physical layer OAM (PLOAM): A message-based operation and management channel between the OLT and the ONUs that supports the PON TC-layer management functions, including ONU activation, OMCC establishment, encryption configuration, key management and alarm signaling.
Optical Carrier (OC): An optical carrier is the standard unit of measure for the rate of transmission bandwidth for data being carried by Synchronous Optical Networking (SONET) fiber-optic networks
Optical Channel (OCh): The optical channel (OCh) sometime referred to as OC is an information structure consisting of the information payload (OCh_PLD) with a certain bandwidth and nonassociated overhead (OCh_OH) for management of the optical channel. For xWDM network, an optical channel refers to a specific transmission channel identified by wavelength or frequency.
Pre-assigned Delay (PrD): The requisite delay that all the ONUs on the PON are required to use prior to completion of the ranging phase of the activation process.
Quiet window: A time interval during which the OLT suppresses all the bandwidth allocations to the in-service ONUs in order to avoid collisions between their upstream transmissions and the transmission bursts from the ONUs that have just joined the PON and are undergoing the activation process.
Ranging: A procedure of measuring the logical distance between the OLT and each of its subtending ONUs with the objective to accurately time the individual ONU upstream transmission bursts so that these bursts arrive at the OLT in a collision-free sequential fashion and the upstream overhead, which is required to ensure burst detection and delineation, is minimal. Ranging is performed during the ONU activation and may be performed while the ONU is in service.
Requisite delay: A general term denoting the total extra delay the OLT may require an ONU to apply to the upstream transmission beyond the ONU's regular response time. The purpose of the requisite delay is to compensate for variation of propagation and processing delays of individual ONUs, and to avoid or reduce the probability of collisions between upstream transmissions.
Status Reporting DBA (SR-DBA): A method of dynamic bandwidth assignment that infers the dynamic activity status of the traffic- bearing entities within optical network units (ONUs) based on the explicit buffer occupancy reports communicated over the embedded OAM channel.
Traffic-Monitoring DBA (TM-DBA): A method of dynamic bandwidth assignment that infers the dynamic activity status of the traffic- bearing entities within optical network units (ONUs) based on the observation of the idle GEM frame transmissions in place of granted upstream bandwidth allocations.
Transmission Container (T-CONT): A traffic-bearing object within an ONU that represents a group of logical connections, is managed via the ONU management and control channel (OMCC), and is treated as a single entity for the purpose of upstream bandwidth assignment on the PON.
U-plane: A plane of the G-PON protocol suite that handles user data in a G-PON system. U-Plane provides communication between GEM clients.
2. Glossary & Acronyms
For more abbreviations and acronyms, please refer to ITU-T G.987 or G.989.
1:N - Splitter ratio
25G-PON - 25 Gbit/s capable Passive Optical Network (its optical specification is based on the IEEE 802.3ca 25G EPON standard and its Transmission Convergence layer is an extension of existing XGS-PON)
4G - Fourth Generation mobile network infrastructure
50G-PON - 50 Gbit/s capable Passive Optical Network
5G - Fifth Generation mobile network infrastructure
AB - Assured Bandwidth allocation (T-CONT type 2,3,5)
ACL - Access Control List
AES - Advanced Encryption Standard
Alloc-ID - Allocation Identifier (12-bit number assigned by the OLT to ONUs)
ANI - Access Node Interface
APC - Angled Physical Contact (type of connector end face, e.g. SC-APC)
A-PON - ATM Passive Optical Network
ARPU - Average Revenue Per User
ATM - Asynchronous Transfer Mode (data transmission technology)
B-PON - Broadband Passive Optical Network (ITU-T)
BCH - Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquengham (cyclic error correction code)
BE - Best Effort bandwidth allocation (T-CONT type 4,5)
BER - Bit Error Ratio
BIP - Bit-Interleaved Parity (error detection)
Blen - BWmap Length
BW - Bandwidth
BWmap - Bandwidth Map. Timeslot assigned to ONUs for upstream transmission
C-PON - 100 Gbit/s Passive Optical Network (in roman numerals C = 100). Also known as 100G Coherent Passive Optical Networks (100G CPON)
CE - Circuit Emulation
CEx - Coexistence Element
CIR - Committed Information Rate
CO - Central Office
COS - Class Of Service (IEEE 802.1p)
CPE - Customer Premises Equipment
CPL - Change Power Level
CRC - Cyclic Redundancy Check (error detection and correction)
CSP - Communication Service Provider
CWDM - Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing
DA - Destination Address
DAA - Distributed Access Architecture
DACT - Deactivate (ONU-ID)
dB - Decibels (relative measure of power gain or loss)
DBA - Dynamic Bandwidth Assignment
dBm - Decibel-milliwatt (measure of power level, referenced to 1 mW)
DBR - Dynamic Bandwidth Report
DBRu - Dynamic Bandwidth Report upstream
DEMUX - Demultiplexer
DF - Deactivate Failure
DG - Dying Gasp
DIS - Disable (ONU serial number)
DOCSIS - Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification
DOW - Drift of Window
DPoE - DOCSIS Provisioning of EPON
DS - Downstream
DUT - Device Under Test
DW - Downstream Wavelength
DWDM - Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing
E2E - End To End
E-PON - Ethernet Passive Optical Network (IEEE)
E/O - Electrical-to-Optical conversion
EBS - Excess Burst Size
EFM - Ethernet in the First Mile
EIR - Excess Information Rate
EMS - Element Management System
EOF - End Of Frame
EqD - Equalization Delay
F1/F2 - Multi-fiber cables connecting 1st and 2nd stage splitters
FB - Fixed Bandwidth allocation (T-CONT type 1,5)
FC - Ferrule Connector (type of 2.5mm fiber optic connector)
FDH - Fiber Distribution Hub
FEC - Forward Error Correction
FSAN - Full Service Access Network
FTTB - Fiber To The Building
FTTC - Fiber To The Curb or Cabinet
FTTH - Fiber To The Home
FTTM - Fiber To The Mobile station
FTTO - Fiber To The Office
FTTP - Fiber To The Premise
FTTW - Fiber To The WLAN
FTTx - Generic for FTTB, FTTH, FTTP, etc.
FUT - Fiber Under Test
FWDM - Filtered Wave-Division Multiplexer
G-PON - Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (ITU-T)
GE - Gigabit/s Ethernet
GEM - GPON Encapsulation Method
GIS - Geographic Information (management) System
GLID – Group Link ID (identifier)
GTC - GPON Transmission Convergence frame
HEC - Header Error Control code or Hybrid Error Correction
HFC - Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial access network architecture
ID - Identifier
IEC - International Electrotechnical Commission (international standardization body)
IEEE - Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (international standardization body)
IF - Interface (also written I/F)
IFgpon - GPON Interface
IP - Internet Protocol
ISP - Internet Service Provider
ITU-T - International Telecommunication Union - Telecom (international standardization body)
LAN - Local Area Network
LC - Lucent Connector (type of 1.25mm fiber optic connector)
LCDG - Loss of Channel Delineation for GEM
LCF - Laser Control Field
LIM - Line Interface Module
LOA - Loss of Acknowledgement
LOAM - Loss of Operations, Administrations and Maintenance
LoB - Loss of Burst
LoDS - Loss of Downstream Synchronization
LOF - Loss of Frame
LOK - Loss of Key
LoOC - Loss of OMCI Channel
LoPC - Loss of PLOAM Channel
LOS - Loss of Signal
LROAN - Long-Reach Optical Access Network
LSB - Least Significant Bit
LTS - Loss Test Set (test equipment)
MAC - Media Access Control address
MDU - Multi-Dwelling Unit (e.g., apartment building)
ME - Managed Entity
MIB - Management Information Base
MIC - Message Integrity Check (security)
MIS - (link) Mismatch
MLID - Management Link ID (identifier)
MPO - Multi-fiber Push-On connector (also known as MTP)
MSA - Multi-Source Agreement (agreement among multiple manufacturers to make compatible products)
MSB - Most Significant Bit
MSO - Multiple System Operator (often refer to cable TV providers offering multiple services, such Internet and phone)
MTP - Multi-fiber Push-On connector (also known as MPO)
MTU - Multi-Tennant Unit (e.g., office building)
MUX - Multiplexer
mW - Milliwatt (unit of power)
NAB - Not Assured Bandwidth allocation (T-CONT type 3,5)
NE - Network Element
NG-PON2 - Next Generation Passive Optical Network (ITU-T)
nm - Nanometer (wavelength)
NMS - Network Management System
NNI - Network-to-Network Interface
NOC - Network Operation Center
NRZ - Non Return to Zero
NSR - Non-Status-Reporting
NSR-DBA - Non Status Report DBA
NTE - Network Termination Equipment
O/E - Optical-to-Electrical conversion
OAM - Operation And Maintenance
OCC - Optical Channel Checker (multi-wavelength meter, test equipment)
OCM - Optical Channel Monitor (xWDM multi-wavelength meter, test equipment)
OCM - Optical Control Module (RFTS, fiber monitoring)
ODN - Optical Distribution Network (includes fibers and splitters between OLT and ONU/ONT). PON and FTTx are examples of ODN.
OLT - Optical Line Terminal
OLTS - Optical Loss Test Set (test equipment)
OMCC - ONU Management and Control Channel
OMCI - ONU Management and Control Interface
ONT - Optical Network Terminal (ITU-T)
ONU - Optical Network Unit (IEEE)
ONU-ID - OND Identifier
OOS - Out Of Service
OPM - Optical Power Meter (test equipment)
OpS - Operations System
OSA - Optical Spectrum Analyzer (test equipment)
OSI - Open Systems Interconnection reference model
OSM - Optical Switching Module (RFTS)
OSP - Outside Plant
OSS - Operations Support System
OTDR - Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer (test equipment)
P2MP - Point-to-Multi-Point
P2P - Point To Point (link or network architecture)
PC - Physical Contact (type of connector end face, e.g. SC-PC)
PCB - Physical Control Block
PCBd - Physical Control Block downstream
PDU - Protocol Data Unit
PEE - Physical Equipment Error
PHY - Physical Interface
PIR - Peak Information Rate
PLEND - Payload Length Downstream field
PLI - Payload Length Indication
PLID - Physical Link ID (identifier)
PLO - Physical Layer Overhead
PLOu - Physical Layer Overhead upstream
PLOAM - Physical Layer Operations, Administration and Maintenace messages
PLOAMd - PLOAM downstream
PLOAMu - PLOAM upstream
PLOu - Physical Layer Overhead upstream
PLS - Power Level Sequence
PLSu - Power Level Sequence upstream
PMD - Physical-Medium-Dependent layer (optical interface)
POL - Passive Optical Local area network
PON - Passive Optical Networks (point-to-multipoint architecture)
PON-T - PON Terminating equipment.
PON ID - PON Identifier
Port ID - Port Identifier
PPTP - Physical Path Termination Point
PrD - Pre-assigned Delay
PSN - Packet Switching Network (e.g., Ethernet)
PST - Passive optical network Section Trace
PSync - Physical Synchronization
PTI - Payload Type Indicator
PW - Pseudowire circuit emulation
QoE - Quality of Experience
QoS - Quality of Service
RDI - Remote Defect Indication
RDOF - Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (USA initiative to promote the construction and operation of rural broadband networks)
REI - Remote Error Indication
RFoG - Radio Frequency Over Glass
RFTS - Remote Fiber Test System (fiber monitoring)
RMS - Root-Mean-Square
RS - Reed Solomon
RTD - Round Trip Delay
RTU - Remote Test Unit (centralized test head or probe consisting of OTDR and optical switches)
SA - Sleep Allow
SC - Subscriber Connector (type of 2.5mm fiber optic connector)
SD - Signal Degrade
SDU - Service Data Unit
SF - Signal Failure
SFD - Start Frame Delimiter
SIR - Sustained Information Rate
SLA - Service Level Agreement
SN - Serial Number
SNI - Service Node Interface
SMNP - Simple Network Management Protocol
SOR - Standard OTDR Record (trace file)
SP - Strict Priority
SR - Status Reporting or Sleep Request
SR-DBI - Status Report DBA
SUF - Start Up Failure
T-CONT - Transmission Containers
TC - Transmission Convergence layer
TDM - Time Division Multiplexing
TDMA - Time Division Multiple Access
Telco - Telephone Company (now offering multiple services, such Internet and video)
TF - Transmitter Failure
THz - Terahertz (frequency)
TLS - Tunable Laser Source
TM - Traffic Monitoring
Type 1 - Transmission container (T-CONT) with fixed bandwidth
Type 2 - Transmission container (T-CONT) with assured maximum bandwidth
Type 3 - Transmission container (T-CONT) with assured bandwidth and maximum burst capabilities
Type 4 - Transmission container (T-CONT) with best effort bandwidth
Type 5 - Transmission container (T-CONT) with mixed bandwidth types
TWDM-PON - Time and Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network
ULID - User Link ID (identifier)
UNI - User-to-Network Interface
UPC - Ultra Physical Contact (type of connector end face, e.g. LC-UPC)
US - Upstream
UW - Upstream Wavelength
VLAN - Virtual Local Area Network
V-TEST - VeEX's Internet Access Speed Test
WBF - Wavelength Blocking Filter
WDM - Wavelength Division Multiplexing
WDM-PON - Wavelength-Division Multiplexing Passive Optical Network
WFM - Work From Home (telecommuting)
WLAN - Wireless Local Area Network (e.g., Wi-Fi)
WMS - Web Map Service
WRR - Weighted Round Robin algorithm
X-haul - Generic for Fronthaul, Midhaul and Backhaul cellular communication links
XG-PON - 10 Gbit/s capable Passive Optical Network (asymmetrical)
XGEM - XG-PON Encapsulation Method
XGS-PON - 10 Gbit/s capable Symmetrical Passive Optical Network
XG(S)-PON - Generic for XG and XGS PON
XGTC - XG-PON Transmission Convergence protocol layer
xWDM - Generic for DWDM and CWDM
λ - Lambda. Represents a laser wavelength (nm)
3. Standards, Specifications & Reference Documents
3.1 ITU-T Recommendations
GPON
G.984.1 - Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (G-PON) general characteristics.
G.984.2 - Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (G-PON) Physical Media-Dependent (PMD) layer specification.
G.984.3 - Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (G-PON) Transmission Convergence (TC) layer specification.
G.984.5 - Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (G-PON): Enhancement band.
G.984.6 - Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (GPON): Reach extension.
G.984.7 - Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (GPON): Long reach.
XG(S)-PON
G.987 - 10-Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (XG-PON) systems: Definitions, abbreviations and acronyms.
G.987.1 - 10-Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (XG-PON): General requirements.
G.987.2 - 10-Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (XG-PON): Physical Media Dependent (PMD) layer specification.
G.987.3 - 10-Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (XG-PON): Transmission Convergence (TC) layer specification.
G.987.4 - 10-Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (XG-PON): Reach extension.
G.9807.1 - 10-Gigabit-capable Symmetric Passive Optical Network (XGS-PON).
G.9807.2 - 10 Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Networks (XG(S)-PON): Reach extension.
NG-PON2
G.988 - ONU Management and Control Interface (OMCI) specification.
G.989 - 40-Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (NG-PON2): Definitions, abbreviations and acronyms.
G.989.1 - 40-Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (NG-PON2): General requirements.
G.Suppl.63 - ITU-T G.989.3 TC layer operating in ITU T G.987.3 or ITU-T G.9807.1 TC layer mode.
3.2 IEEE Recommendations
EPON
IEEE 802.3ah - IEEE Standard for Information technology. Part 3: CSMA/CD Access Method and Physical Layer Specifications: Media Access Control, Physical Layers, and Management Parameters for Subscriber Access Networks (EPON - Section 60)
IEEE 802.3bk - IEEE Standard for Ethernet IEEE Std 802.3-2012: Physical Layer Specifications and Management Parameters for Extended Ethernet Passive Optical Networks
10G EPON
IEEE 802.3av - IEEE Standard for Information technology. Part 3: CSMA/CD Access Method and Physical Layer Specifications: Physical Layer Specifications and Management Parameters for 10Gbps PON (10G-EPON Sections 75 to 77)
High Speed EPON (25G/50G/100G)
IEEE 802.3ca - Standard Project for Ethernet Amendment: Physical Layer Specifications and Management Parameters for 25 Gbps and 50 Gbps Passive Optical Networks
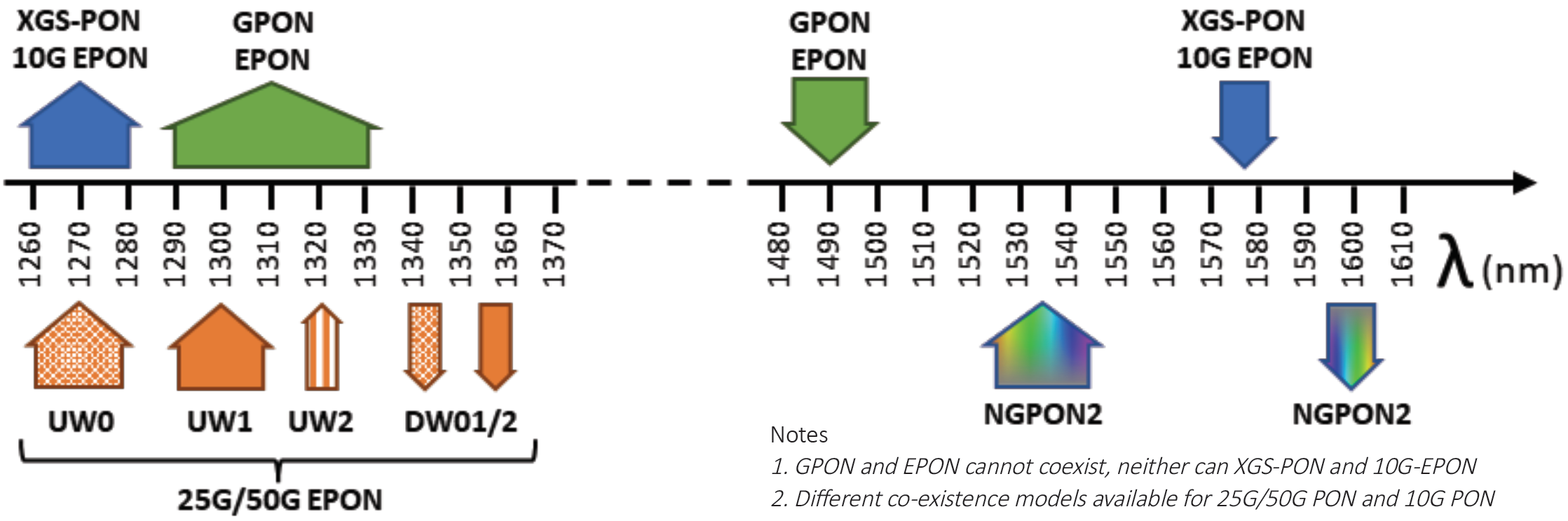
4. Wavelength Reference Guide
Related Test Solutions
