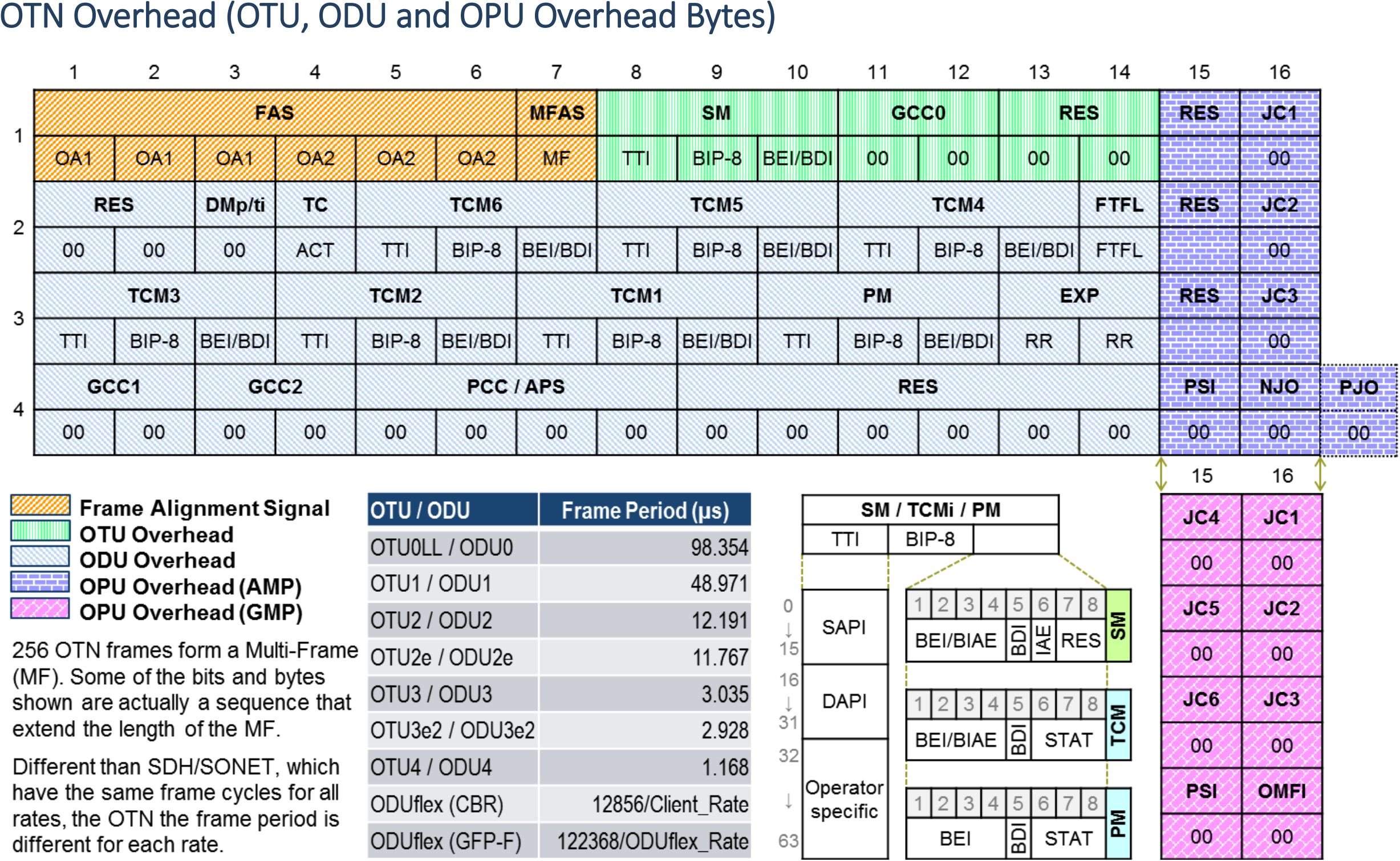
OTN Glossary & Quick References
List of technical terms, abbreviations, acronyms, references, errors and alarms used in Optical Transport Networks (ITU-T G.709)
Refer to the OTN Reference Guide document for more details
Table of Contents
1. General OTN Acronyms & Terminology
3R - Re-amplification, Reshaping and Retiming
ACO - Analog Coherent Optics
ACT - TC Activation/deactivation control channel
AIS - Alarm Indication Signal
AMP - Asynchronous Mapping Procedure
API - Access Point Identifier
APS - Automatic Protection Switching (refer to PCC)
B100G - Beyond 100 Gbit/s (refers to newer technologies like OTUCn, FlexO and FlexE)
BCH - Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem (forward error correction mechanism)
BDI - Backward Defect Indication
BER - Bit Error Rate
BERT - Bit Error Rate Test
BEI - Backward Error Indication
BIAE - Backward Incoming Alignment Error (interleaved-bit blocks errors detected in the upstream direction)
BIP-8 - Bit Interleaved Parity (error detection flag calculated over the whole OPU and payload and inserted into the SM header two frames later)
BMP - Bit-synchronous Mapping Procedure
CAUI - 100G Attachment Unit Interface (100 = C in roman numerals)
CBR - Constant Bit Rate
cFEC - Correctable FEC error count
CFEC - Concatenated (Cascaded) FEC. Combines outer SC-FEC and inner SD-FEC codes, producing significantly improved performance compared to GFEC
CFP - C Form-factor Pluggable interface module (C = 100G). Available in CFP, CFP2 and CFP4 sizes
CMx - Portions of the Alignment Markers common to all lanes
CPRI - Common Public Radio Interface (cellular)
CSOC - Convolutional Self-Orthogonal Code
DAPI - Destination Access Point Identifier
DCO - Digital Coherent Optics
DMp - Delay Measurement - Path level
DMti - Delay Measurement - TCM level i
DP-QPSK - Dual Polarization Quadrature Phase Shift Keying modulation
DSP - Digital Signal Processor
EXP - Experimental
EFEC - Enhanced FEC
EoOTN - Ethernet over OTN
FAS - Frame Alignment Signal (OH)
FC - Fibre Channel
FEC - Forward Error Correction
fgGMP - Fine Grain Generic Mapping Procedure (fgOTN)
fgODUflex - Flexible p x 10 Mbit/s transport container for fgOTN (1 ≤ p ≤ 119, to fill a traditional 1.25G container)
fgOPU - Fine Grain Optical Payload Unit (fgOTN)
fgOTN - Fine Grain OTN. Newer p x 10 Mbit/s map/mux sub-rate structure defined by ITU-T G.709.20
fgTS - Fine Grain Teibutary Slot (fgOTN)
FlexE - Flexible Ethernet (defined by OIF)
FlexO - Flexible OTN (ITU-T G.709.1)
FOIC - FlexO Interface
FTFL - Fault Type / Fault Location channel (this 256-byte multi-frame signal provides fault status information, type and location)
Gbit/s - Gigabit per second
Gbps - Gigabit per second
GCC - General Communication Channels (GCC0, GCC1, GCC2). Overhead bytes.
GCC0 - General Communication Channel (two-byte communication channel between section end points)
GCC1 - General Communication Channel (communication between two NEs)
GCC2 - General Communication Channel (communication between two NEs)
GE - Gigabit Ethernet
GFEC - Generic FEC. The original Reed-Solomon RS(255,239)
GFP - Generic Framing Procedure
GFP-F - GFP Framed
GFP-T - GFP Transparent (transcoding)
GID - FlexO Group ID
GMP - Generic Mapping Procedure
HAO - Hitless Adjustment of ODUflex(GFP) signals
HO - Higher Order (H)
IaDI - Intra-Domain Interface (within operator's domain)
IAE - Incoming Alignment Error
IEC - Incoming Error Count
IMP - Idle Mapping Procedure
IrDI - Inter-Domain Interface (between operators) with 3R processing
JC - OPU Justification Control (3 bytes for AMP and 6 for GMP). Overhead byte.
JOH - Justification Overhead
KP4 - Reed-Solomon RS(544,514,10) FEC from IEEE 802.3
MAP - FlexO overhead field for the OTUC to FlexO PHY mapping
LDPC - Low Density Parity Check
LL - Logical Lane
LO - Lower Order (L)
LSS - Loss of test Sequence Sync (pattern loss)
LTC - Loss of Tandem Connection
MF - Multi-Frame
MFAS - Multi-Frame Alignment Signal (OH)
MSI - Multiplexer Structure Identifier (OPU)
NCG - Net Coding Gain achieved by adding FEC (improvements in OSNR)
NJO - OPU (AMP) Negative Justification Opportunity (pointer). Overhead byte.
NNI - Network to Network Interface
NRZ - Non-Return to Zero data modulation (On-Off Keying, OOK)
OADM - Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer
OAM - Operation and Maintenance
OBSAI - Open Base Station Architecture Initiative (cellular)
OCC/OCCr - Optical Channel Carrier (r = reduced functionality)
OCh/OChr - Optical Channel (r = reduced functionality)
ODTUCn - ODTU for multiplexing an ODU signal into an OPUCn
ODTUCn.ts - ODTU for multiplexing an ODU into Tributary Slots of an OPUCn
ODTUG - Optical channel Data Tributary Unit Group
ODTUjk - Optical channel Data Tributary Unit, j into k
ODTUk.ts - Optical channel Data Tributary Unit, with tributary slots
ODU - Optical channel Data Unit
ODUflex - ODU with flexible Nx1.25 Gbit/s capacity
ODUflex(CBR) - Flexible rate ODU for carrying CBR client signals
ODUflex(GFP) - Flexible rate ODU for carrying packet client signals that use a GFP-F mapping into the OPUflex
ODUflex(IMP) - Flexible rate ODU for carrying packet client signals with Ethernet Idle characters used for rate adaptation when mapping into the OPUflex
ODUk - Optical channel Data Unit, level k (k = 1 to 4)
ODUk(H) - Higher order ODUk (Multiplexed clients)
ODUk(L) - Lower order ODUk (Direct client mapping)
ODUk-Xv - X virtually concatenated ODUk's
oFEC - Open FEC (used in OpenZR+ and Open ROADM)
OH - Overhead
OMFI - OPU Multi-Frame Identifier (GMP) OTU4. Overhead byte.
OMS - Optical Multiplex Section
OPS - Optical Physical Section
OPSM - Optical Physical Section Multi-Lane
OPU - Optical channel Payload Unit
OPUk - Optical channel Payload Unit, level k
OSC - Optical Supervisory Channel
OSMC - OTN Synchronization Message Channel
OSNR - Optical Signal-to-Noise Ratio
OTL - Optical Channel Transport Lane
OTLk.n - Optical channel Transport Lane
OTLCx - Optical channel Transport Lane Carrier (x = optical lane)
OTM - Optical Transport Module
OTN - Optical Transport Networks (formerly known as "Digital Wrapper")
OTP - Optical Transport Platform
OTS - Optical Transmission Section
OTU1 - 2.66 Gbit/s
OTU2 - 10.7 Gbit/s
OTU2e - 11.09 Gbit/s (used for 10GE payloads)
OTU3 - 43 Gbit/s
OTU3e - 44.58 Gbit/s (used for 40GE payloads)
OTU4 - 111.8 Gbit/s
OTUCn - n x 100 Gbit/s OTN, beyond 100G
OTUk - Optical channel Transport Unit, level k (1 to 4)
OWD - One-Way Delay (one-way latency)
OXC - Optical Cross-Connect equipment
P-OTN - Packet OTN
P-OTP - Packet Optical Transport Platform
PAM4 - Phase-Amplitude Modulation, four levels
PCC - Protection Communication Channel (Up to eight levels of nested APS/PCC signals)
PCS - Physical Coding Sub-layer
PID - FlexO PHY ID
PJO - Positive Justification Opportunity (pointer). Overhead byte.
PM - Path Monitoring (ODUk)
PMD - Physical Medium Dependent sub-layer (Ethernet)
PRBS - Pseudo Random Bit Sequence (test pattern)
post-FEC - Errors detected (remaining) after forward error correction (also uFEC)
pre-FEC - Errors detected before forward error correction
PSI - Payload Structure Identifier (OPU). Overhead byte
PT - Payload Type
PT20 - 2.5G ODU multiplex structure (old) ODTUjk
PT21 - 1.25G multiplexing (new) ODTUjk & ODTU.ts
QAM - Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
QSFP - Quad SFP transceiver (up to 40 Gbit/s, NRZ)
QSFP+ - Enhanced QSFP transceiver (up to 40 Gbit/s, 4x10G NRZ)
QSFP28 - Enhanced QSFP transceiver (up to 112 Gbit/s, 4x28G NRZ)
QSFP56 - 200G QSFP transceiver (up to 200 Gbit/s, 4x56G PAM4)
QSFP-DD - 400G QSFP Double Density (up to 400 Gbit/s, 8x56G PAM4)
RES - Reserved for future use (OH)
ROADM - Reconfigurable Optical Add/Drop Multiplexer
RS - Reed-Solomon (FEC)
RTD - Round Trip Delay
SAPI - Source Access Point Identifier
SC-FEC - Hard-Decision StairCase FEC
SD-FEC - Soft-Decision Hamming FEC
SDT - Service Disruption Time
SFP - Small Form-factor Pluggable transceiver
SFP+ - Enhanced SFP transceiver (up to 16 Gbit/s, NRZ)
SFP-DD - Double Density SFP (100 Gbit/s, 2x56G PAM4)
SFP28 - 28G SFP transceiver (25 Gbit/s, NRZ)
SFP56 - 56G SFP transceiver (50 Gbit/s, 56G PAM4)
STAT - Path Monitoring Status bits (3)
SM - Section Monitoring (OTUk)
TC - Tandem Connection
TCM - Tandem Connection Monitoring (enables signal monitoring across different networks or operators)
TCMi - Tandem Connection Monitoring channel (i = 1 to 6)
TDM - Time Division Multiplexing (e.g., SDH/SONET, PDH, DSn)
TIM - Trace Identification Mismatch (warning indicator)
TS, T/S - Tributary Slot
TSE - Test Sequence Error (bit error or test pattern error)
TTI - Trail Trace Identifier (tributary label)
TTT - Timing Transparent Transcoding (compressed)
uFEC - Uncorrectable FEC error count
UMx - Portions of the Alignment Markers unique to each lane
UNI - User to Network Interface
WDM - Wavelength Division Multiplexing
XFP - 10G Form-factor Pluggable interface module (10 = X in roman numerals)
XLAUI - 40G Attachment Unit Interface (40 = XL in roman numerals)
2. OTN Errors & Alarms (Anomalies & Defects)
2.1 Optical Physical Layer
LOS - Loss of Signal
2.2 OTL - Optical channel Transport Lane
ERRORS
LLM - Logical Lane Marker Error
FAS - Logical Lane Frame Alignment Error
MFAS - LL Multi-Frame Alignment Error
ALARMS
LOL - Loss of logical Lane alignment (Two or more logical lanes with the same marker. Consecutive LLM errors for ≥ 5 frames)
OOL - Out of logical Lane (LL) alignment
OOF - LL Out of Frame (FAS error for ≥ 5 frames)
LOF - LL Loss of Frame (consecutive OOF for ≥ 3ms)
OOR - Out of Recovery (wrong LLM value for ≥ 5 cycles)
LOR - Loss of Recovery (consecutive OOR for ≥ 3ms)
OOLLM - Out of Logical Lane Marker (LLM errors for ≥ 5 frames)
OOMFAS - Out of LL MFAS (MFAS errors for ≥ 5 frames)
High Skew - Skew for any of the lanes is greater than a threshold (limit) value set for the application
2.3 OTU – Optical Transport Unit
ERRORS
FAS - Frame Alignment Signal Error (mismatch)
• One or more framing bits in error
MFAS - Multi-Frame Alignment Signal error (mismatch)
• MFAS indicator (0 to 255) is in error (out of sequence)
SM-TIM - Trail Trace Identifier Mismatch
• Received and expected TTI are different
SM-BIP-8 - Bit Interleaved Parity - level 8 code error (mismatch)
• Received and calculated BIP are different
SM-BEI - Backward Error Indication (BEI/BIAE bits)
• 0..8 Number of BIP-8 violations detected
• 9..A No BIP-8 error detected
• B Refer to BIAE
• C..F No BIP-8 error detected
SM-BIAE - Backward Incoming Alignment Error (BEI/BIAE bits)
• B (1011) ≥ 3 consecutive frames
cFEC - Corrected FEC errors (don’t affect ODUk payload)
uFEC - Uncorrectable FEC errors (ODUk payload is affected)
ALARMS
OOF - Out of Frame
• FAS errors ≥ 5 consecutive frames
LOF - Loss of Frame
• When in OOF condition for ≥ 3 ms
OOM - Out of Multiframe
• MFAS errors for ≥ 5 consecutive frames
LOM - Loss of Multiframe
• When in OOM condition for ≥ 3 ms
SM-BDI - Backward Defect Indication
• Defect: Set to 1 for ≥ 5 consecutive frames
• Normal: Set to 0 for ≥ 5 consecutive frames
SM-IAE - Incoming (Frame) Alignment Error
• Defect: Set to 1 for ≥ 5 consecutive frames
• Normal: Set to 0 for ≥ 5 consecutive frames
OTU-AIS - Alarm Indication Signal
• Repetitive PN-11 sequence (2^11-1) completely filling OTUk frames
2.4 ODU-PM – Path Monitoring
ERRORS
PM-BIP-8 - Bit Interleaved Parity - level 8 code error (mismatch)
• Received and calculated BIP are different
PM-TIM - Trail Trace Identifier Mismatch
• Received and expected TTI are different
PM-BEI - Backward Error Indication (BEI/BIAE bits)
• 0..8 Number of BIP-8 violations detected
• 9..F No BIP-8 error detected
ALARMS
PM-BDI - Backward Defect Indication
• Defect: Set to 1 for ≥ 5 consecutive frames
• Normal: Set to 0 for ≥ 5 consecutive frames
ODU-LCK - Locked
• Defect: STAT = 101 for ≥ 3 consecutive frames, plus all PM bytes (except FTFL) and payload filled with 0101 0101
• Normal: STAT = 001
ODU-OCI - Open Connection Indication
• Defect: STAT = 110 for ≥ 3 consecutive frames, plus all PM bytes (except FTFL) and payload filled with 0110 0110
• Normal: STAT = 001
ODU-AIS - Alarm Indication Signal
• Defect: STAT = 111 for ≥ 3 consecutive frames
• Normal: STAT = 001
2.5 ODU TCMi – Tandem Connection Monitoring
ERRORS
TCM-BIP-8 - Bit Interleaved Parity - level 8 code error (mismatch)
• Received and calculated BIP are different
TCM-TIM - Trail Trace Identifier Mismatch
• Received and expected TTI are different
TCM-BEI - Backward Error Indication (BEI/BIAE bits)
• 0..8 Number of BIP-8 violations detected
• 9..A No BIP-8 error detected
• B Refer to BIAE
• C..F No BIP-8 error detected
ALARMS
ODU-LTC - Loss of Tandem Connection
TCM-BDI - Backward Defect Indication
• Defect: Set to 1 for ≥ 5 consecutive frames
• Normal: Set to 0 for ≥ 5 consecutive frames
TCM-LCK - Locked
• Defect: STAT = 101 for ≥ 3 consecutive frames
• Clear: STAT ≠ 101
TCM-OCI - Open Connection Indication
• Defect: STAT = 110 for ≥ 3 consecutive frames
• Clear: STAT ≠ 110
TCM-AIS - Alarm Indication Signal
• Defect: STAT = 111 for ≥ 3 consecutive frames
• Clear: STAT ≠ 111
TCM-BIAE - Backward Incoming Alignment Error (BEI/BIAE bits)
• B (1011) ≥ 3 consecutive frames
2.6 FTFL – ODU Fault Type and Fault Location Reporting
Byte 0 - Forward Fault Type Identification
• 00 No fault
• 01 Signal fail
• 02 Signal degrade
• 03..FF Reserved
Bytes 1..9 - Operator identifier field (forward) Downstream
Bytes 10..127 - Operator-specific field (forward) Downstream
Byte 128 - Backward Fault Type Identification
• 00 No fault
• 01 Signal fail
• 02 Signal degrade
• 03..FF Reserved
Bytes 129..137 - Operator identifier field (backward)
Bytes 138..255 - Operator-specific field (backward)
2.7 OPU – Optical Payload Unit
ERRORS
PLM - Payload Label Mismatch (Expected and received Payload Types, first byte of the PSI sequence, are different)
OMFI - OPU Multi-Frame Identifier Error (OTU4 ODTU.M only)
LO-OMFI - Loss of OMFI
OO-OMFI - Out of OMFI
2.8 GMP – Generic Mapping Procedure
ERRORS
LO-Sync - Loss of Synchronization
Cm=0 - No payload
CRC-5 - CRC-5 Error
CRC-8 - CRC-8 Error
2.9 PRBS - Test Pattern/Sequence in Payload
ERRORS
Bit - Bit Error (also known as Test Sequence Error)
LSS - Loss of test Sequence Synchronization (pattern loss)
TSE - Test Sequence Error (also known as Bit Error)