How to Use Ramp Mode for Ethernet Traffic Generation
What is Ramp Mode?
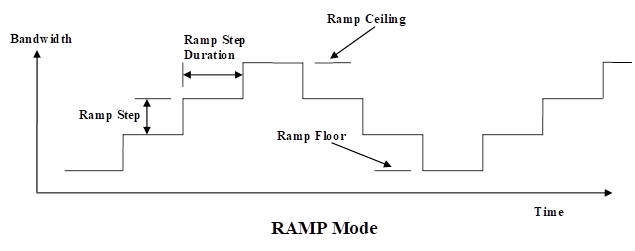
Ramp Mode is an Ethernet Traffic Generation method that continuously steps up and down the Ethernet transmit bandwidth % or Mbps rate.
Ramp mode is a feature that is commonly used to simulate a dynamic increasing and decreasing traffic load on a network device.
This is normally performed to monitor a network device’s performance, under these varying loads. This mode can also be used as a stress test, when the traffic increase is set to a very steep rate change.
Configuration Settings: (using the MPA's WebUI)
- Select the Ethernet's Traffic tab.
- Click the edit icon
 for the test stream(s) to configure their Traffic Stream Profile(s).
for the test stream(s) to configure their Traffic Stream Profile(s). - Select the Rate menu in the Traffic Schedule, and select either Ramp L1 Bandwidth %, or Ramp L1 Mbps.
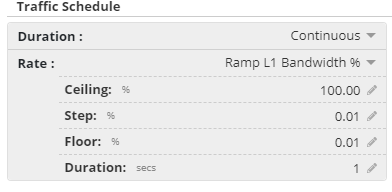
- Ceiling: This is the maximum % Bandwidth, or Mbps rate, that you want the stream traffic to step up to.
- Step: This is the size of the % Bandwidth, or Mbps rate, that each step (up and down) should change by.
- Floor: This is the minimum % Bandwidth, or Mbps rate, that the stream will step down to.
- Duration: This is the period of time (from 1 to 999 second) that each step (up and down) will transmit for.
How to Test with Ramp Mode:
- Verify you have round-trip continuity by temporarily enabling the test stream(s) and verify that both the TX and RX Packet counts are increasing.
- Turn OFF the test stream(s), and press the port's Restart buttons on both the MPA and the device under test (DUT) to clear any previous packet count history.
- Next, back turn ON the test stream(s) that are configured for Ramp Mode.
- Monitor the network DUT for anomalies, as the traffic being generated repeatedly steps up and steps back down again, increasing and decreasing its RX traffic load until the test is stopped.
- Turn OFF the test streams and verify that the DUT’s RX Packet count matches the MPA’s TX Packet count.
